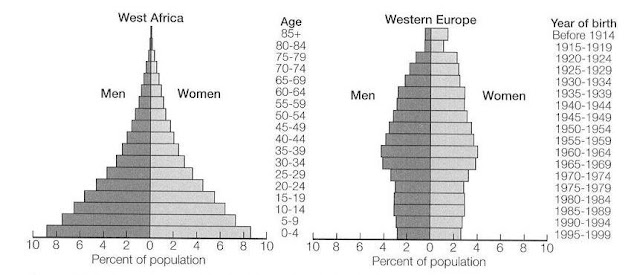
The gravity of Europe’s demographic situation became clear at a conference I attended in Singapore last year. Dieter Salomon, the green mayor of the environmentally correct Freiburg, Germany, was speaking about the future of cities. When asked what Germany’s future would be like in 30 years, he answered, with a little smile, ”There won’t be a future.”
Herr Mayor was not exaggerating. For decades, Europe has experienced some of the world’s slowest population growth rates. Fertility rates have dropped well below replacement rates, and are roughly 50% lower than those in the U.S. Over time these demographic trends will have catastrophic economic consequences. By 2050, Europe, now home to 730 million people, will shrink by 75 million to 100 million and its workforce will be 25% smaller than in 2000._JoelKotkin_Forbes
When a welfare state is in the throes of a shrinking demographic, the implications are extremely dire. Guarantees of benefits in these nations is based upon a pyramid scheme, with the older pensioners near the apex and the younger taxpayers near the base. If the positions are reversed due to a collapsing demographic, national debt tends to grow to massive proportions rather quickly.
The fiscal costs of this process are already evident. Countries like Spain, Italy and Greece, which rank among the most rapidly aging populations in the world, are teetering on the verge of bankruptcy. One reason has to do with the lack enough productive workers to pay for generous pensions and other welfare-state provisions.
Germany, the über-economy of the continent, has little hope of avoiding the demographic winter either. By 2030 Germany will have about 53 retirees for every 100 people in its workforce; by comparison the U.S. ratio will be closer to 30. As a result, Germany will face a giant debt crisis, as social costs for the aging eat away its currently frugal and productive economy. According to the American Enterprise Institute’s Nick Eberstadt, by 2020 Germany debt service compared to GDP will rise to twice that currently suffered by Greece. _Forbes_Kotkin
The United States under Obama has been trying to imitate the European style of government -- a designed expansion of the public sector at the expense of the private sector. Fortunately for Obama -- in one sense -- the US is not suffering the same demographic collapse as Europe. The US is instead still growing demographically, due to immigration and due to higher birthrates among immigrants.
But in another sense, the US population growth is not as fortunate as it appears. The new replacement populations coming into the US are, on average, of lower aptitude in a cognitive sense. Average IQ of the US population is almost certain to drop as a result, and US global comptetiveness will be strained, consequently.
Trends in SAT test scores are an early warning of this very phenomenon:
"The scores are disappointing, and it seems to be a trend over the last five to six years, with drops across the board," said Jim Hull, senior policy analyst for the National School Board Association's Center for Public Education.
He called 10 points "a pretty significant change."
"It raises a red flag," he said. _WashingtonExaminer
Test score drops will be blamed on a number of factors, but the studiously ignored central cause of this trend is the lowered cognitive potential of modern students. And it is only likely to get worse. And the repercussions of this cognitive decline will spread throughout society -- and will be magnified tenfold by affirmative action policies.
The SAT has already been "dumbed down," perhaps in anticipation of this very phenomenon, but apparently it was not dumbed down enough. It will probably not be long before the ACT follows suit, in politically correct fashion. More: Steve Sailer takes a closer look at changes in SAT scores over the past several years, with stratification of scores by race.
A dumber population will place greater demands on governmental infrastructure. Law enforcement, welfare, education, housing, food subsidies, etc. will all have to grow more productive to compensate for a population of lower cognitive aptitudes.
National debt will increase even faster than at present, as the underlying society grows less capable of repaying their own debt on top of the debt of previous generations. Economic hardship will increase.
Multicultural societies are low-trust societies, which require much larger police forces to maintain order. As police forces are downsized due to the exponential growth in public sector union pensions and benefits, civil disorder will expand to fill the void.
Youth gangs made up almost entirely of immigrants, children of immigrants, and "minority" populations, will range the landscape virtually unimpeded by a law enforcement infrastructure that will grow more corrupt as it takes on the multi-cultural form of the new dominant populations of society. The initiation ritual for many of these gangs is likely to be an act of violence against the shrinking population of the formerly dominant, European descended people.
Can you and yours find a place of safety in this coming world? That depends upon what you do between now and then.
Hope for the best. Prepare for the worst.
Previously published on abu al-fin
For the architects of the Next Level, this dumbed down demographic -- a de facto Idiocracy -- presents special challenges. It will require working through alternative infrastructures other than traditional governmental institutions.
The creation of such "shadow governments" will not be easy, but it will not necessarily be as expensive as one might think. More on that later.